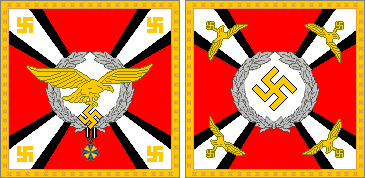
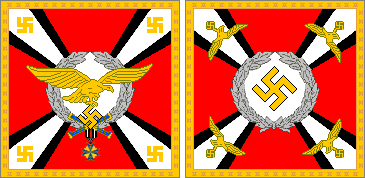
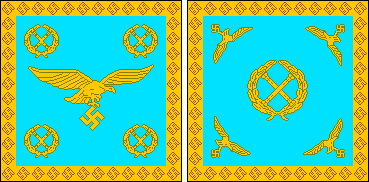
GREATER GERMAN REICH
COMMAND FLAGS OF THE LUFTWAFFE • 1935-45