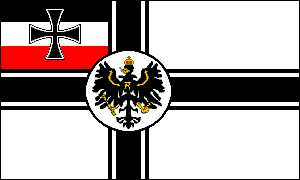
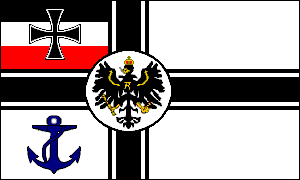
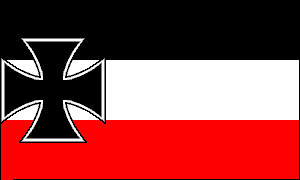
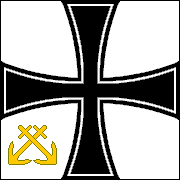
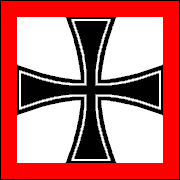
GERMAN EMPIRE
NAVAL ENSIGNS & FLAGS • 1871-1918