RUSSIAN EMPIRE
UNIT MARKER FLAGS • 1866 REGULATIONS
Images Added August 2015
Rifle Battalion • Pioneer Battalion
| FIRST INFANTRY REGIMENT OF THE FIRST BRIGADE |
|||
| FIRST BATTALION | SECOND BATTALION | ||
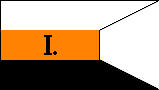 |
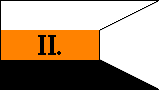 |
||
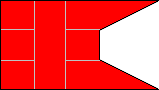 1st Company |
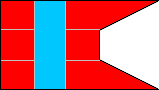 2nd Company |
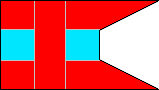 5th Company |
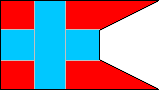 6th Company |
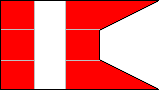 3rd Company |
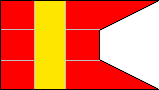 4th Company |
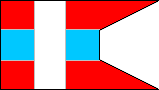 7th Company |
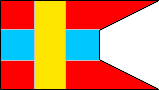 8th Company |
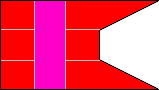 1st Rifle Company |
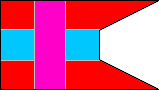 2nd Rifle Company |
||
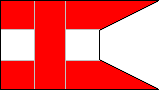
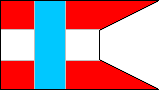
| THIRD BATTALION | FOURTH BATTALION | ||
 |
 |
||
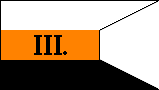
 9th Company |
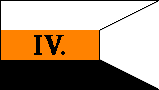
 10th Company |
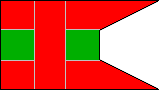 13th Company |
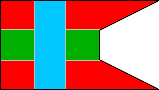 14th Company |
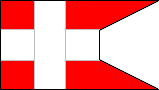 11th Company |
 12th Company |
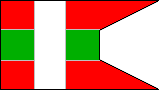 15th Company |
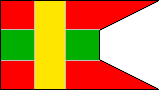 16th Company |
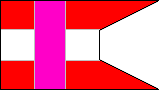 3rd Rifle Company |
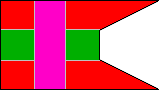 4th Rifle Company |
||
|
INFANTRY TRAINING BATTALION |
|||
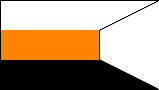 |
|||
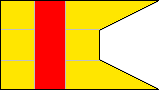 1st Company |
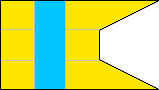 2nd Company |
||
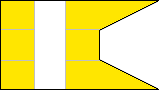 3rd Company |
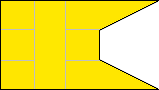 4th Company |
||
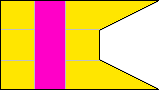 Rifle Company |
|||
|
RIFLE BATTALION |
PIONEER BATTALION |
||
 |
 |
||
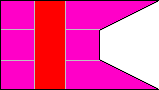 1st Company |
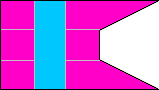 2nd Company |
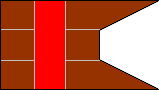 1st Company |
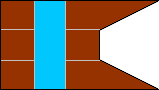 2nd Company |
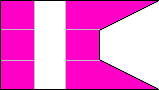
3rd Company |
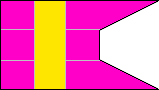
4th Company |
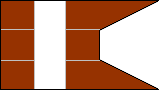
3rd Company |
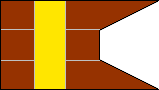
4th Company |