|
|
|
From ST. ANDREW'S CROSS to YACHT ENSIGN |
|
|
|
Bold print in the body of a definition indicates that the word or term has its own entry. |
|
|
|
From ST. ANDREW'S CROSS to YACHT ENSIGN |
|
|
|
Bold print in the body of a definition indicates that the word or term has its own entry. |
S
St. Andrew's Cross: (1) the national flag of Scotland and emblem of its patron saint, a blue flag charged with a white saltire; (2) one of the three crosses forming the British Union Jack (see also Andrew Flag).
St. Andrew's Cross (Scotland)
St. David's Cross: a traditional flag of Wales and emblem of its patron saint, a black flag divided by a yellow cross into four equal quarters.
St. David's Cross (Wales)
St. George's Cross: (1) the national flag of England and its patron saint, a white flag divided by a red cross into four equal quarters; with or without red disks in the hoist quarters it serves as a flag of rank for admirals of the Royal Navy below the rank of Admiral of the Fleet; (2) one of the three crosses forming the British Union Jack (see also New England Flag).
St. George's Cross (England)
St. Patrick's Cross: (1) a traditional flag of Ireland and emblem of its patron saint, a white flag charged with a red saltire; (2) one of the three crosses forming the British Union Jack; (3) the flag of the US state of Alabama, adopted because of its resemblance to the Confederate Battle Flag.
St. Patrick's Cross (Ireland)
saltire: a diagonal cross (see also Andrew Flag, Confederate Battle Flag, St. Andrew's Cross, St. Patrick's Cross).
Savoy Cross: a red flag divided by a white cross into four equal quarters, with or without a blue border; actually a banner of arms of the House of Savoy, the former Italian royal family; the flag with blue border was formerly the Italian jack.
The Savoy Cross (Italy)
Scandinavian Cross: a flag divided by a cross whose vertical arm is offset toward the hoist; so called because this cross is the principal design element of the flags of the Scandinavian countries, e.g. Sweden (see also Dannebrog, Splittflag).
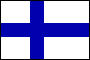
Scandinavian Cross Flags, Finland & Norway
Serapis Ensign: an historical American flag, flown by John Paul Jones during the famous action between his ship, Bon Homme Richard, and the British frigate HMS Serapis off Flamborough Head, Yorkshire (23 September 1779); the design featured a blue canton with thirteen white stars and a field of red, white and blue stripes (see also war ensign).
The Serapis Ensign
shift colors: US Navy term for the procedure whereby a warship's National Ensign and Union Jack are struck from their staffs at the bow and stern and the ensign is rehoisted at the mainmast as the ship gets underway, and for the reverse procedure which is followed when the ship moors or anchors.
signal flags: flags or sets of flags designed for the transmission of visual signals, especially between ships at sea (see also bunting-tosser, dress ship, flag bag, Flags).
Southern Cross: a representation of the constellation of the same name, used on the flags of many nations in the South Pacific region, e.g. Australia, New Zealand and Western Samoa.
National Flags of Australia & New Zealand with the Southern Cross
Splittflag: the forked version of the Danish flag, used as Denmark's war ensign, war flag, and, with or without additional badges, for various other official purposes, e.g. the Danish state ensign is the Splittflag with a white royal crown in the canton (see also Dannebrog).
The Danish Splittflag
Stainless Banner: popular nickname for the second (first official) flag of the Confederate States of America, adopted 1863, which was white with the Confederate Battle Flag as a canton; in 1865 it was modified by the addition of a wide vertical red stripe at the fly end (see also Stars and Bars).
The Stainless Banner (1863-65)
standard: (1) the heraldic flag of a nobleman; (2) the regimental color of a cavalry regiment (see also banner of arms, guidon, Royal Command Flag, royal flag, Royal Standard, vexillum).
The Heraldic Standard of John, Lord Camoys (England, 15th Century)
Standard of the United States: until ca. 1850, the National Color for infantry regiments of the US Army; a dark blue flag charged with the Coat of Arms of the United States over a scroll bearing the regimental title; it was carried with a regimental color charged with a regimental insignia or badge; when a version of the US national flag was adopted as the National Color by the Army, the Standard of the United States became the regimental color (see also Organizational Color, two-color system).
stand of colors: a set of military colors, e.g. the Queen's Colour and Regimental Colour of an infantry regiment of the British Army.
Stars and Bars: popular nickname for the first (unofficial) national flag of the Confederate States of America, which had horizontal stripes or bars of red, white and red, and between seven and thirteen white stars in a blue canton; used 1861-65 despite the adoption of the Stainless Banner in 1863 (see also Bonnie Blue Flag, Confederate Battle Flag).
The Stars and Bars (1861)
Stars and Stripes: popular nickname for the US national flag derived from its design elements, a field of horizontal stripes and a canton with stars (see also Continental Colors, First Navy Jack, "Great Star" flags, Merchant Stripes, Old Glory, Star Spangled Banner, union, Union Jack).
Star Spangled Banner, The: (1) the US national anthem; Francis Scott Key composed the lyrics in 1814 and the tune was taken from an old British drinking song, "To Anacrenon in Heaven"; (2) popular nickname for the Fort McHenry Flag, which still exists and is on display in Washington, DC; (3) popular nickname for the US national flag generally (see also "Great Star" flags, Old Glory, Stars and Stripes).
The Star-Spangled Banner (1814)
state ensign: an ensign for non-naval government vessels, e.g. vessels belonging to the customs service.
State Ensign (UK)
state flag: (1) the version of a country's national flag used for official purposes when variants exist, e.g. the state flag of Norway which is a forked ensign, defaced with an appropriate badge (postal, customs, etc.); (2) the flag of a US state.

State Flags, Finland & Germany
streamer: in the US armed forces, a narrow length of ribbon with a swallowtailed fly end, which is attached to the top of the staff of an Organizational Color or Organizational Flag to signify a battle honor, campaign credit or unit decoration; streamers are generally made in the colors of the appropriate campaign medal or decoration; those used by the Army and Air Force bear an inscription denoting the action for which the unit was cited or the campaign in which it participated; those used by the Navy and Marine Corps bear bronze or silver stars to denote actions and campaigns; those used by the Coast Guard are plain (see also regimental color).
US Army Campaign Streamer (Civil War)
strike the colors: to lower the flag, especially in naval practice as a token of surrender.
T
Taunton Flag: historical American flag, the British Meteor Flag with the inscription "LIBERTY and UNION" applied in white along the lower edge; raised on Taunton Green, Massachusetts Bay colony, 19 October 1774 in protest against British tax policies; made the official flag of the City of Taunton (US) on 19 October 1974 (see also Continental Colors, New England Flag).
The Taunton Flag
"To the Color": in the US armed forces, the bugle call sounded when the National Color is raised or lowered; during a retreat ceremony "To the Color" precedes the playing of the National Anthem.tongued ensign: see forked ensign.
tricolor: (1) a flag of three colors divided into three vertical or horizontal stripes; the basic design element of a large number of flags worldwide; (2) popular name for the French national flag, which consists of equal vertical stripes of blue, white and red (cap. Tricolor).
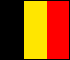
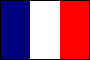

Tricolor Flags of Belgium, France, Italy & Russia
troop the colour (UK): to parade regimental colors before the regiment; originated ca. the 17th century as a means to insure that soldiers would recognize their own colors in battle; nowadays "Trooping the Colour" is a traditional ceremony performed by the Brigade of Guards on the Queen's Birthday.
two-color system: British system for military colors, introduced in the 18th century, whereby each regiment is granted two colors, one a variant of the national flag and one a regimental color; the two-color system is used in most Commonwealth countries and also in the US (see also National Color, Organizational Color, Queen's Colour, Standard of the United States).
U
union: term sometimes used to describe the canton of the US national flag, dark blue with fifty white stars (see also Union Jack, Stars and Stripes).
Union Jack: (1) the UK state flag and jack, a design combining the crosses of the patron saints of England (St. George), Scotland (St. Andrew) and Ireland (St. Patrick), adopted 1 January 1801 in connection with the formation of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland; an earlier version, adopted in 1606, omitted St. Patrick's Cross; though technically the Union Jack is a royal flag, in practice it serves as the national flag of the UK; also known as the Union Flag; (2) the US jack, actually the canton or union of the US National Ensign, dark blue with 50 white stars (see also St. Andrew's Cross, St. George's Cross).
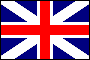
The Union Jack, 1606-1801 & Since 1801
Union Mark: device used in the canton of Swedish and Norwegian flags and ensigns during the period of these countries' personal union under the Swedish Crown (1815-1905); the device consisted of four triangles joined to form a square; the left and right triangles displayed the Swedish cross while the top and bottom ones displayed the Norwegian cross.
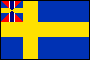
Swedish & Norwegian National Flags with Union Mark Canton
V
vessel flag: in the US Army, a branch-oriented distinguishing flag flown from vessels and watercraft.
vexillology: the scientific study of flags and their history.
vexillum: ancient Roman cavalry standard, suspended from a crossbar (see also guidon).
Vierkleur Flag: "Four Color Flag"; the 1858-1902 flag of the Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek (South African Republic), combining the horizontal red, white and blue stripes of the Dutch flag with a vertical green stripe at the hoist. Used unofficially as the flag of the Transvaal Province (Union, later Republic, of South Africa) up to 1994.
National Flag, South African Republic, 1858-1902
W
war flag: a variant or alternate national flag flown over military installations on land; often identical to the state flag and/or the war ensign, as in Denmark (see also air force ensign, army service flag).
War Flag of the Republic of China, 1912-28
war ensign: see naval ensign.
White Ensign: the naval ensign of the UK, originally (17th century) a white flag with the St. George Cross in the canton; in 1702 a white flag quartered by a red cross with the St. George Cross in the canton; in 1707 the first Union Jack was substituted in the canton; in 1801 the second Union Jack was substituted in the canton; a number of Commonwealth countries, e.g. the Bahamas, use a similar naval ensign with their national flags in the canton (see also battle ensign).
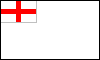
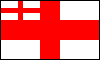
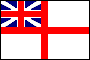
UK White Ensigns, 17th century, 1702, 1707 & since 1801
Y
yacht ensign: a special version of a nation's civil ensign which is authorized to be flown by yacht club members, e.g. the US yacht ensign is a variant of the National Ensign with a white foul anchor enclosed by a circle of 13 white stars in the union; in other countries, e.g. the UK, many individual yacht clubs are granted distinctive ensigns based on the Blue Ensign or Red Ensign.

Yacht Ensigns, Royal Victoria Yacht Club (UK) & National Yacht Club (Ireland)
![]()