|
|
|
From AIR FORCE ENSIGN to GUIDON |
|
|
|
Bold print in the body of a definition indicates that the word or term has its own entry. |
|
|
|
From AIR FORCE ENSIGN to GUIDON |
|
|
|
Bold print in the body of a definition indicates that the word or term has its own entry. |
A
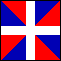
air force ensign: in numerous countries, a variant of the national flag flown over air force installations; many are based on the Royal Air Force (UK) Ensign, being light blue with the national flag as a canton and the air force insignia (roundel) in the fly (see also civil air ensign).
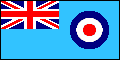
Air Force Ensigns, UK & India
Andrew Flag: common nickname for the war ensign designed for Russia by Peter the Great circa 1700, a white flag with a blue saltire; so called because it is a variant of the St. Andrew's Cross; abolished in 1918 by the Bolshevik government but readopted 1991; defaced with the Royal Arms of Scotland it also serves as the flag of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.
The Andrew Flag (Russian Federation)
army service flag: a variant of the national flag for army use, e.g. the South African Army Flag; not to be confused with regimental colors (see also war flag).

Army Service Flags, China & Egypt
aspect ratio: the proportions of a flag, e.g. 2:3 denoting a flag that is two units of measurement at the hoist by three units of measurement on the fly.
B
banner of arms or armorial banner: a flag made by rendering the shield of a coat of arms in square or rectangular banner form, e.g. the Royal Standards of British monarchs (see also Banner of France, presidential flag, Royal Command Flag, royal flag, standard).
Banner of Arms (Scotland)
Banner of France: a blue flag charged with three gold French lilies or fleurs-de-lise; actually a banner of the French royal arms; numerous variants existed between the 12th and 18th centuries, e.g. a white flag with gold fleurs-de-lise, sometimes defaced with the full royal arms.
The Banner of France
battle ensign or (US Navy) battle color: a large war ensign hoisted by warships for ease of identification during naval engagements or, generally, whenever a warship's nationality must be readily distinguishable.
Bear Flag: historical American flag of the California Republic, ca. 1840, and the current state flag of California; the name derives from the flag's principal charge, a bear.
bicolor: a flag of two colors divided vertically or horizontally into equal halves, e.g. the Landesfarben flags of many German states and territories.
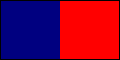

Bicolor Flags of Haiti, Indonesia & Ukraine
Blood Banner (Ger. Blutfahne): the Nazi Party flag which, during the Munich Beer Hall Putsch (8-9 November 1923), was carried on the march that ended in a gun battle between the Nazis and the Bavarian State Police; so called because it was stained with the blood of several Party members who were killed or wounded in the exchange of fire; became a Nazi Party icon and the central symbol in many Nazi ceremonies.
Blue Ensign: (1) a dark blue flag with the Union Jack as a canton; defaced with an appropriate badge in the fly it serves as the flag of a number of British dependent territories, past and present, e.g. the Falkland Islands, and also as the ensign for various state agencies of the UK; with no badge it is flown by merchant vessels commanded by officers of the Royal Naval Reserve; (2) Blue Ensigns defaced with stars arranged in the form of the Southern Cross constellation are the national flags of Australia and New Zealand.
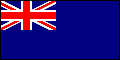
Blue Ensigns, Royal Naval Reserve & Royal Fleet Auxiliary Service (UK)
boat flag: small version of an ensign for ships' boats.Bonnie Blue Flag, The: (1) a blue flag charged with a single large white star, the unofficial flag of the South in the years immediately preceding the Civil War; similar in design to the current national flag of Somalia; (2) the song of the same name, composed in 1860 and popular in the South throughout the Civil War (see also Stainless Banner, Stars and Bars).
The Bonnie Blue Flag
broad pennant: the naval flag of rank of a commodore, often, e.g. in the Royal Navy (UK), a forked and tapered version of the rear admiral's flag of rank.
Broad Pennant of a Commodore (France)
Bunker Hill Flag: flag believed to have been used by the American colonists at the Battle of Bunker Hill (Boston, Massachusetts Bay colony, 17 June 1775); though many sources show it as blue with a canton of the St. George's Cross, charged in its first quarter with a green pine tree, the actual Bunker Hill Flag was probably red with a green pine tree in a white canton (see also New England Flag).
The Bunker Hill Flag
bunting tosser, Bunts: traditional nicknames in the Royal Navy (UK) for sailors in the signals branch whose duties include the care and hoisting of signal flags, ensigns, etc.
C
Canadian Red Ensign: the former quasi-official national flag and official civil ensign of Canada, replaced in 1965 by the Maple Leaf Flag; it was a British colonial ensign of the standard pattern, being red with the Union Jack as a canton and the shield of the Canadian coat of arms in the fly; adopted in its original form ca. 1867; a Canadian Blue Ensign also existed, which served as the government ensign and naval jack; it was identical to the Red Ensign except for its field color; also replaced by the Maple Leaf Flag in 1965 (see also Red Ensign, Blue Ensign).
The Canadian Red Ensign (1922-57 Version)
canton: the upper left-hand portion of a flag; usually but not always the canton is one-fourth of the flag's total area (see also quarter).
charge: term adopted from heraldry; the application of design elements to a flag, e.g. the St. George Cross flag of England is white, charged with a red cross.
chief: term adopted from heraldry; the upper half of a flag.
civil air ensign: a variant of the national flag which is flown over civil air installations, e.g. the UK civil air ensign, a light blue flag charged with a dark blue cross, fimbriated white, with the Union Jack as a canton (see also air force ensign).
civil ensign or merchant ensign: an ensign for non-naval, non-government vessels.

Civil Ensigns, Germany (1919-33) & Australia (Current)
civil flag: the version of a country's flag used by individuals and non-government organizations on land, when variants exist for official purposes; usually informally called the national flag; an example is the German civil flag, a black-red-golden yellow horizontal tricolor (the versions of this flag for official government use are defaced with the state coat of arms).

Civil Flags, Austria & Germany
coat of arms: heraldic insignia usually consisting of a shield, crest, supporters and motto; coats of arms or their elements appear in the designs of numerous flags, e.g. the colonial ensigns of the UK (see also banner of arms, Banner of France, Green Flag, Organizational Color, presidential flag, Royal Command Flag, Royal Crest, royal flag, Royal Standard).
colonel's color: 18th-century term for the senior regimental color; applied to those systems which allotted a color to each company of the regiment, one of which was the "colonel's company," one the "lieutenant-colonel's company" etc.; ceased to apply in Britain when the two-color system was adopted there; survived in France where infantry regiments continued to carry a colonel's color and a variable number of drapeaux d'ordannance until the Napoleonic era.
England: Colonel's Color, Lord Lucas' Regiment or 34th Foot (ca. 1705)
color: military term for a flag, e.g. National Color, regimental color; a color is usually ornamented with a fringe, tassels, etc. (see also Organizational Color).
color-bearing unit: in the US Army, the term for any formation entitled to an Organizational Color.
color guard (US) or colour party (UK): a military escort for colors.
colors: (1) collective military and naval term for flags and ensigns, e.g. strike the colors; (2) in the US armed forces, the daily raising and lowering of the National Flag or National Ensign (see also "To the Color").
commissioning pennant: a long, narrow pennant with a forked or pointed fly end, usually incorporating design elements of the national flag; flown from the mast of a warship to show that it is in service ("in commission") and under the command of a commissioned naval officer.
Confederate Battle Flag: flag introduced in 1862 for battlefield use by the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia, as the Stars and Bars too closely resembled the US flag at a distance; the basic design was a red flag charged with a blue saltire, fimbriated white, bearing 13 white stars; usually though not always made square with a white border but many variations existed; with no white border appeared as the canton of the second and third Confederate national flags; in 2:3 proportions with no white border served as the Confederate Navy's jack; (see also Stainless Banner, St. Patrick's Cross).
The Confederate Battle Flag
Continental Colors: the first US national flag, with a field of seven red and six white alternating horizontal stripes, and the British Union Jack (first version without the St. Patrick's Cross) as a canton; the design was an adaptation of the Meteor Flag intended to express the colonists' unity in their demand for the traditional rights of Englishmen; never officially adopted by Congress but in use 1775-77 (see also New England Flag, Taunton Flag).
The Continental Colors
cornet: (1) 18th-century term for a cavalry regiment's standard or guidon; (2) rank title formerly applied to the junior officer of cavalry entrusted to bear the regimental standard (see also regimental color).
Cornwall Cross: traditional flag of Cornwall (England); a black flag charged with a white cross.
The Cornwall Cross
courtesy ensign: flag hoisted at the foremast by any ship when visiting a foreign port, usually the civil ensign of the host nation.customs flag: flag identifying installations of a nation's customs service, most often flown at border crossing and ports of entry; sometimes a variant of the state flag and sometimes, e.g. in the US, a distinctive flag flown together with the national flag.
Customs Flag (US)
customs ensign: flag flown by vessels of a nation's customs service, often a variant of the state ensign.
D
Dannebrog: the national flag of Denmark; possibly the oldest national flag still in use today, having been adopted in the 11th century; a red flag charged with a white cross, the vertical arm being offset toward the hoist (see also forked ensign, Scandinavian cross, Splittflag).
The Dannebrog (Denmark)
deface or defacement: alteration of a flag by the addition of a badge or other symbol to the basic design, e.g. the defaced Union Jacks flown by governors of British dependent territories.
dip the flag or dip the colors: to salute with a flag; at sea this is done by lowering and then rehoisting the ship's ensign; on land, usually in connection with military ceremonies, it is done by lowering the flagstaff from the vertical position to a diagonal position; these military customs and practices vary by country but in the US, the National Color is never lowered in salute.
drapeau d'ordannance (pl. drapeaux d'ordannance; Fr.): term applied to regimental colors carried by the French infantry in the pre-Revolutionary period (ca. 16th-18th centuries); literally it means "flag of regulation" and refers to the fact that such flags originated as markers by means of which the line of troops were dressed; most were divided by a white cross into four quarters which varied in color and design by regiment; the number of drapeaux d'ordannance authorized per regiment varied over time from two to fourteen (see also colonel's color).
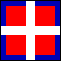
Drapeaux d'Ordannance (ca. 1760)
dress ship: naval custom by which a warship hoists all its flags as a sign of celebration; nowadays signal flags are employed for this purpose.
E
eagle: term applied to the regimental colors carried by the armies of Napoleon, 1804-1815, especially those of the infantry; the name derives from the fact that the actual flag was affixed to a pole topped by a gilt eagle, this being the primary Imperial emblem; the flag itself was a variant of the Tricolor, inscribed on the obverse with the regimental title and on the reverse with the regiment's battle honors.
Color of the Foot Grenadiers of the Imperial Guard (France)
ensign: (1) a national flag or variant thereof for use at sea or for some other special purpose, e.g. the air force ensigns and civil air ensigns used by many nations; (2) in the 17th-18th centuries, a term applied to flags generally, especially military flags; (3) 18th-century military rank title applied to junior officers of infantry regiments entrusted to bear the regimental colors; (4) current rank title of the lowest commissioned rank in the US Navy (see also cornet).
ensign staff: the staff from which a ship's ensign is flown.
F
false colors or false flag: a flag displayed or hoisted to disguise one's intentions, especially during wartime at sea; under international law this is permissible so long as one's proper flag or ensign is hoisted before opening fire.
field: in design terms, the base color of a flag, e.g. the St. Andrew's Cross flag has a blue field charged with a white saltire.
finial: an ornamental device attached to the head of a flagstaff, e.g. the silver spearpoint used for the staffs of US Army flags, colors and guidons.fimbriation: a narrow band in a contrasting color used to separate design elements of a flag.
First Navy Jack: historical US flag consisting of seven red and six white alternating horizontal stripes, charged with the image of a snake and the motto DON'T TREAD ON ME; in use as a US naval flag ca. 1775-1800 until replaced by the current Union Jack; during the year of the US Bicentennial (1976) it was again flown as a jack by all US Navy ships; by regulation it is always flown as a jack by the oldest US Navy ship in regular commission (see also Merchant Stripes).
First Navy Jack (US)
Five-Color Flag: the first national flag of the Republic of China, consisting of equal horizontal stripes of red, yellow, blue, white and black; adopted 1912 and in use until 1928.
The Five-Color Flag of China (1912-28)
flag bag: on ships of the US Navy, the bridge locker in which signal flags are stored.
flag officer: a commissioned military or naval officer entitled to display a flag of rank, e.g. general officers of the US Army, who have scarlet flags with from one to five white stars, depending on rank (see also St. George's Cross, Union Jack).
flag of rank or rank flag: a flag flown by a military or naval officer to denote his rank, e.g. when the Union Jack is flown from the foremast of a ship of the Royal Navy (UK), this indicates the presence aboard of an Admiral of the Fleet (see also flag officer, St. George's Cross).
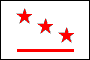
Army Rank Flags, Italy (General of Army Corps) & US (Brigadier General)
Flags: traditional nickname in the US Navy and the Royal Navy (UK) for signalmen, whose duties include the care and hoisting of signal flags, ensigns, etc. (see also bunting-tosser).
fly: the free vertical half of the flag opposite the staff; in illustrations, the fly is shown to the viewer's right (see also hoist).
forked ensign (also tongued ensign): a flag with one or two triangular segments removed from its fly to make pointed "tongues"; found principally in the Scandinavian countries where they are used as war ensigns and/or state ensigns and state flags, e.g. the Danish Splittflag; sometimes called swallowtailed flags (see also broad pennant, Dannebrog; ensign, guidon).
Forked Naval Ensign (Germany)
Fort McHenry Flag: the US national flag with fifteen stars and fifteen stripes that flew over Fort McHenry, Baltimore, Maryland during the British bombardment of 12-13 September 1814; this incident inspired Francis Scott Key to compose the poem that became the US national anthem (see also Star Spangled Banner, The).
fringe: ornamental addition to the three free edges of a flag, especially military flags and colors (see also National Color).
G
government ensign: see state ensign.Grand Union Flag: see Continental Colors.
"Great Star" flags: 19th-century variants of the US national flag on which the white stars in the blue canton were arranged in the shape of a single large star.
A Great Star Flag of 1820 (23 stars)
Green Flag, The: a banner of arms of the ancient Irish province of Leinster, a green flag charged with a gold harp; in official use today as the jack of the Irish Naval Service.
The Green Flag (Irish Naval Service Jack)
guidon: (1) a small forked or swallowtailed marker flag carried by military units below the battalion level (US); (2) the flag or color of a cavalry regiment (UK and British Commonwealth; see also cornet, standard, vexillum).
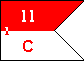
Guidons, US Army (Cavalry Troop) & US Air Force (Security Police Squadron)